Redox flow battery (RFB) is a rechargeable electrochemical device
2022-06-14
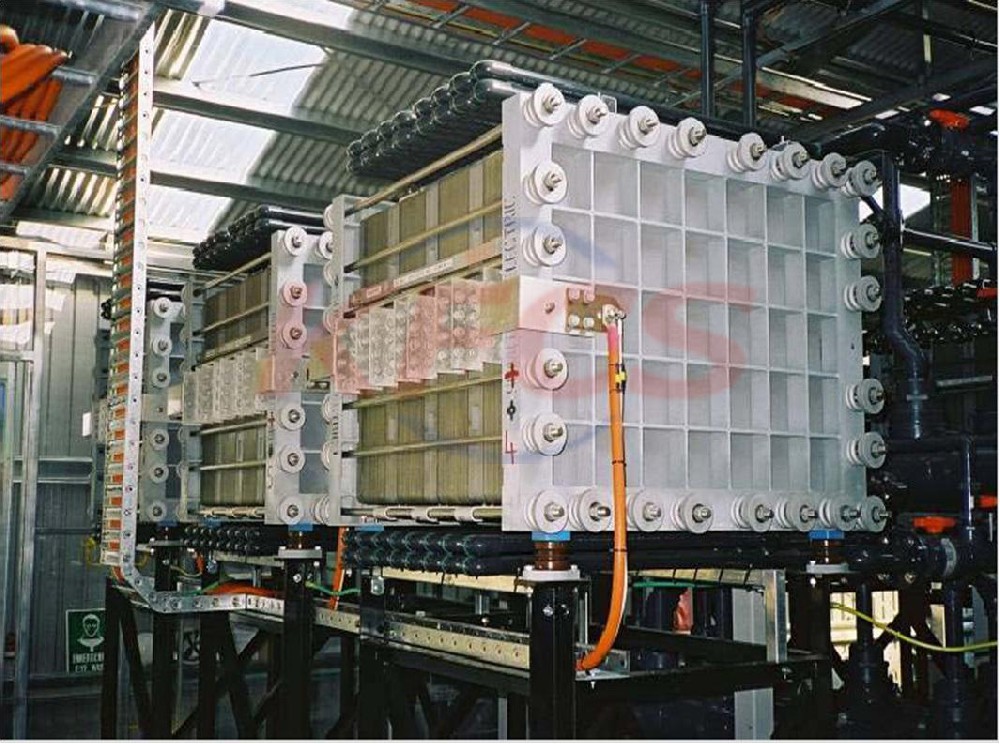
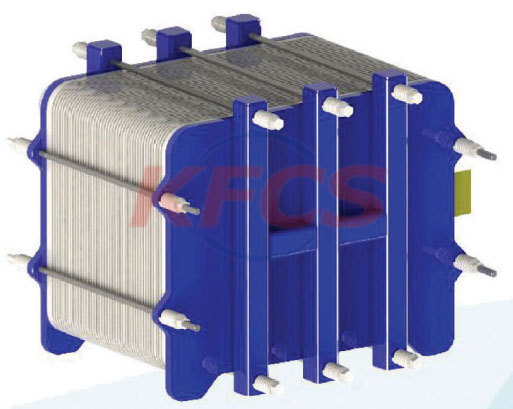
Redox flow battery (RFB) is a rechargeable electrochemical device, in which charge storage substances are dissolved in liquid electrolyte and stored in cheap storage tank, and charge discharge cycle is carried out through power conversion reactor, in which they are oxidized and reduced to alternately charge and discharge the battery. In the reactor, the two electrolytes (usually referred to as "positive electrolyte" and "negative electrolyte" according to their respective electrode potentials) are separated by a proton exchange membrane and reduced and oxidized on the surface of the porous electrode. Ions pass through the proton exchange membrane to balance the charge between the two electrolytes, so as to maintain electrical neutrality and ideally block the charge storage material.
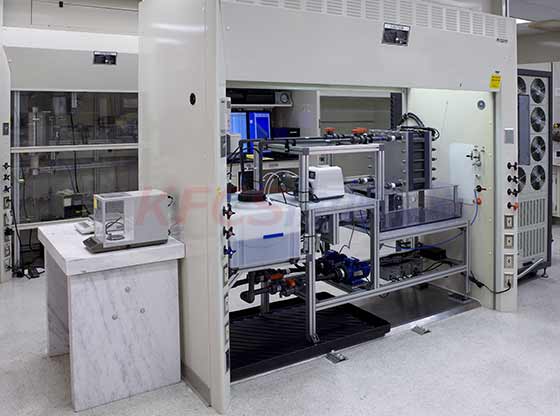
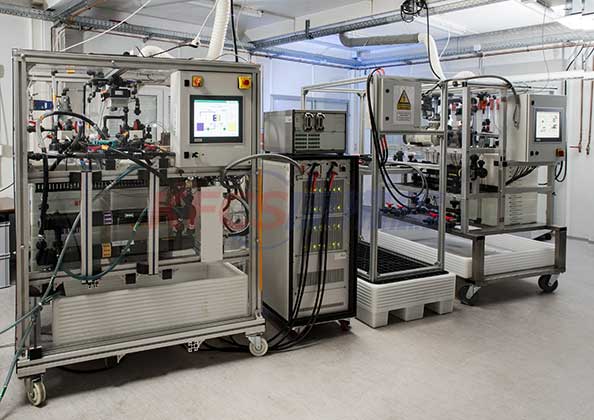
Like other energy storage systems, redox flow battery (RFB) requires equipment balance subsystems to support operation, including fluid, thermal and state of charge management systems.
About News
- Advantages of vanadium redox battery energy storage
- Cold sintering may open door to improved solid-state battery production
- Tiny battery-free sensing device floats with the wind
- New South Wales plans to deploy 700MW/1400MWh battery energy storage projects
- Characteristics Of Vanadium Redox Battery Energy Storage Technology
- Advantages of all-vanadium redox flow batteries
- South African grid operator Eskom plans to deploy 199MW/832MWh battery energy storage project
- Ultra-high-purity lithium can be recycled at low cost
- Application of vanadium battery in farm
- Current large-scale applications of vanadium redox flow batteries
Products